Comparison Overview
IBM and Google performed about the same over high quality reference audio recorded in a quiet setting using a medium quality microphone.
However, IBM was much better able to generate transcripts for lower quality recordings obtained in noisy settings.
Processing seconds per minute : about the same
IBM and Google process the audio in about the same amount of time. Google is somewhat faster; however, it requires that the file be uploaded to Google Storage first.
IBM Transcribed/Processed : 7281/7288
IBM was able to transcribe almost all of the files submitted.
Google Transcribed/Processed : 3521/7343
The transcription rate was lower for two main reasons. One was due to a file size limit. Files larger than ~80MB require an agreement be made with Google, whereas IBM was willing and able to process files of arbitrary size. The second main reason is that Google is less accommodating of noisy recordings. Many files that were below the file size limit failed to generate a transcript. Many more that did had low word counts.
Transcript words per minute of audio (IBM/Google) : 102.0/9.8
Even after adjusting for transcription rate, the number of transcript words generated per minute of audio was much lower for Google.
Comparison on reference documents
The following comparisons were made over 245 reference documents. The reference transcripts were transcribed using a speech-to-text transcription software that was trained to my voice, in a quiet environment, using a hand-held medium quality wired microphone. Most of the errors were manually corrected.
Google generated a transcript for 210 out of the 245 reference documents (86%), and IBM generated a transcript for 243 of the 245 (99%). The Bleu scores over these reference documents are fairly comparable, with IBM performing slightly better.

When measured using Ratcliff-Obershelp similarity, Google fares slightly better across the board.

Comparison over all audio
This comparison is over 8,415 audio files that were submitted to each service.
Marked differences between IBM Watson and Google transcription arise when comparing transcription rates and number of words generated when run on audio collected out in the wild. Of 8,415 such audio, IBM generated transcripts for 7,227, while Google was able to generate a transcript for 3,521.
Total Word Counts
Out of 8,415 audio files attempted, Google generated 3,521 transcripts. Those 3,521 transcripts contain total of 485,334 words, an average of 137 words per transcript.
IBM Watson generated 7,227 transcripts, extracting 9,511,743 words out of those transcripts. This gives an average of 1,316 words per transcript. [TODO: update with April returns]
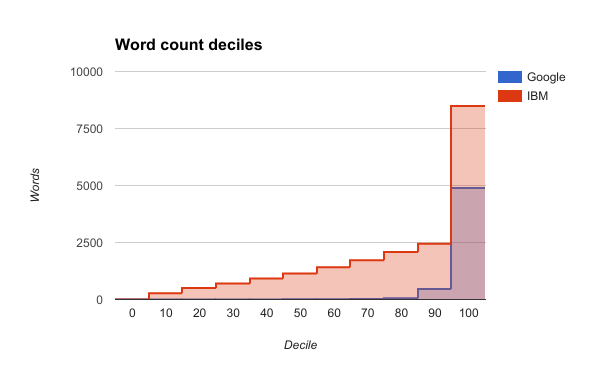
Word Count Deciles
Many of these transcripts that Google failed to generate were simply due to the file size exceeding quota.
However Google also failed to generate any transcript words for many other files that did not exceed the file size quota. It also generated a much lower word count per transcript for audio that was from a noisy or low bit rate recording.
One way to illustrate this is by examining the word count deciles over the transcripts that were successfully generated.
The following table gives the word counts deciles over the transcripts generated by each service.
| API | min | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 12 | 19 | 58 | 459 | 4892 | |
| IBM | 1 | 278 | 501 | 698 | 916 | 1137 | 1409 | 1722 | 2080 | 2450 | 8490 |